Contact resistance refers to the resistance to current flow due to surface conditions and other reasons when the contact surfaces are in contact with each other (in the closed state of the device). This can happen between parts such as disconnector, circuit breakers, relays and switches. The contact resistance test can understand the connection quality of the line and its conductive characteristics, and avoid dangerous overheating of the contacts.

Contact resistance test content
Two common inspections performed on circuit breaker contacts are visual inspection and contact resistance inspection.
1. Visual inspection includes checking the circuit breaker contacts for dents due to arcing and contact wear or deformation.
2. The second check is the contact resistance measurement. This involves injecting a fixed current, usually around 100A, 200A and 300A, through the contacts and measuring the voltage drop across it. This test is done using a special contact resistance measuring instrument. Then, use Ohm's law to calculate the resistance value. The resistance value needs to be compared with the value given by the manufacturer. This value should also be compared with previous records.
These two tests need to be done together. Since there are cases where the contactor has good contact resistance but is still in a damaged state. Therefore, for a contactor to prove healthy, it needs to have good contact resistance and should clear the visual inspection test.
The contacts in the circuit breaker need to be checked regularly to ensure that the circuit breaker is healthy and functioning properly. Poor or poor contact can lead to arcing, loss of phase, and even fire. This test is especially important for contacts that carry large amounts of current, such as switchgear busbars, where higher contact resistance results in lower ampacities and higher losses. Contact resistance tests are usually performed using a micro/milliohm meter or a low ohmmeter. The measurement of contact resistance helps to identify fretting corrosion of contacts and can diagnose and prevent contact corrosion. An increase in contact resistance can cause a high voltage drop in the system and needs to be controlled.
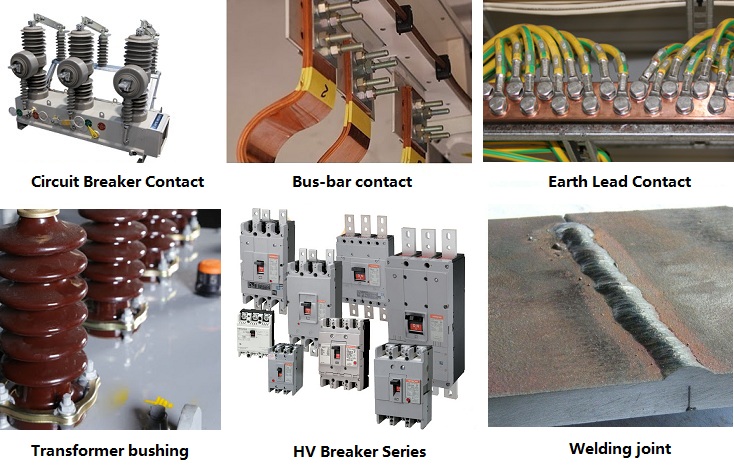
Kingrun series switch (circuit breaker) Contact Resistance Tester / loop resistance tester is widely used for measuring the contact resistance, cable wire and weld contact resistance of various electrical switches.

Kingrun Transformer Instrument Co.,Ltd.


More Transformer Testers from Kingrun
