Transformer bushings are critical components that connect the transformer’s internal windings to external circuits. Their performance directly affects the safety and stability of the power system. Below is an analysis from the perspectives of types, functions, and testing:
1. Types
Based on insulation materials and structural design, transformer bushings can be classified as follows:
Porcelain Bushings: Made of high-strength ceramic materials, these are durable and resistant to environmental interference, representing the traditional form of bushings.
Composite Bushings: Constructed from materials such as epoxy resin and silicone rubber, they are lightweight, resistant to pollution, and offer excellent seismic performance, increasingly replacing porcelain bushings in some applications.
Oil-Impregnated Paper (OIP) Bushings: Internally insulated with oil-impregnated paper, these bushings are suitable for high-voltage levels and are commonly used as the main bushings in transformers.
Capacitive Graded Bushings: Equipped with uniformly distributed capacitive layers to reduce axial electric field gradients and enhance insulation levels, they are widely used in ultra-high voltage (UHV) and extra-high voltage (EHV) transformers.
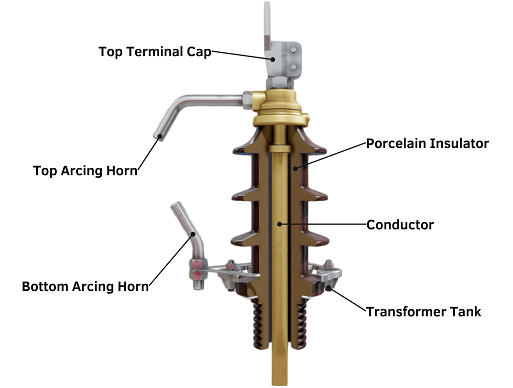
2. Functions
Transformer bushings perform several key functions:
Electrical Insulation: Safely guide the transformer’s high-voltage potential to external connections, preventing arc flashover and partial discharge.
Mechanical Support: Support the conductive connections and withstand external mechanical forces and electrodynamic stresses.
Sealing and Protection: Ensure an oil-tight seal between the bushing and the transformer tank, preventing oil or gas leakage and the ingress of moisture and contaminants.
Electric Field Grading: High-voltage bushings (such as capacitive graded bushings) balance the electric field distribution through capacitive voltage division, reducing local stress concentrations.

3. Testing Items
To ensure reliable performance, typical tests conducted on transformer bushings include:
DC Resistance Measurement: Checks the resistance of conductors and connections to ensure normal conductivity.
AC Withstand Voltage Test: Applies high voltage at power frequency to verify the insulation capability of the bushing.
Partial Discharge Test: Monitors the partial discharge levels under high voltage to assess the condition of the insulation system.
Insulation Resistance Test: Determines whether the bushing insulation is affected by moisture ingress or aging.
Dielectric Dissipation Factor (tan δ) Test: Evaluates the dielectric losses of the insulation material.
Sealing Test: Verifies the oil and gas sealing performance to prevent leakage during operation.
Visual Inspection and Creepage Distance Measurement: Checks the physical condition and verifies the effective creepage distance to prevent pollution flashover incidents.
·
During bushing selection and operation and maintenance, factors such as system voltage level and service environment must be comprehensively considered to determine suitable parameters. Periodic testing and inspections are essential to understand the condition of the bushings and ensure reliable power system operation.
Kingrun Transformer Instrument Co.,Ltd.



More Transformer Testers from Kingrun
