Transformer oil breakdown voltage (BDV) testing is a method to measure the insulation strength of transformer oil by applying high voltage using a testing device. In the early 20th century, BDV testing was a hazardous manual operation. Early equipment used large, exposed high-voltage step-up transformers connected to a simple spark gap immersed in an oil cup.There were no automatic control devices; operators had to manually turn heavy rheostats or "variable transformers" to increase the voltage until a visible and audible arc broke down the oil layer. These devices were housed in thick cast iron or wooden enclosures, lacking the safety interlocks that are common today.
By the 1950s and 1960s, electrode shapes (such as VDE or ASTM spherical electrodes) were standardized in the industry. Testers became more portable, integrating the transformer and oil cup into a "briefcase" design, but still relied on analog meters and manual timing.The digital era transformed BDV testers into "set-and-forget" devices. Modern testers use microprocessors to precisely control the voltage rise rate, detect breakdowns in microseconds, and automatically stir the oil between tests. Today's devices are extremely lightweight and come equipped with built-in printers and Bluetooth functionality.

GTD1001DInsulatingOil Breakdown Voltage (BDV)Tester:
The GTD1001D Insulating oil breakdown voltage tester adopts a completely new electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) concept, designed to prevent tester crashes during testing and to ensure stable operation even in high magnetic fields.
The GTD1001D also uses advanced voltage breakdown control technology, which keeps the breakdown energy at a very low level, preventing contamination of the oil sample during testing and ensuring that the test results are accurate and reliable.
A unique advantage of this tester is its built-in electronic boost system. The voltage regulation power supply utilizes an electronic inverter sine wave generator, providing accurate voltage output with high waveform quality. It is unaffected by grid voltage fluctuations and waveform distortions, which enhances the accuracy and efficiency of the test data. The built-in advanced insulating materials and heat dissipation system ensure that the step-up transformer remains stable and reliable, enabling the tester to withstand long-term high-voltage breakdown tests. This protects operator safety and prolongs the service life of the tester.
4.Complete Protection System:
The GTD1001D includes various protection devices to ensure the safety of both the operator and the tester in cases of faults, such as low breakdown voltage of the oil or empty cup breakdown.
5.Multiple International Testing Standards:
The tester supports fully automatic test sequences for 12 common international standards and spot tests (Standards: ASTM D877 & ASTM D1816, IEC 60156).
6.Internationally Universal Stainless Steel Calipers:
The precise adjustment of standard electrode distances is facilitated by international universal stainless steel calipers.
7.Overall Shielding Technology:
The comprehensive shielding technology prevents all sources of electronic interference, ensuring a pure test environment.
8.Multilingual Technical Instructions:
The tester provides English operation pages and instructions available in 15 languages.
TECHNOLOGY SPECIFICATION:
|
Type |
GTD1001D Insulating Oil breakdown voltage(BDV) tester |
|
Output Voltage Range |
0~80kV |
|
Voltage Resolution |
0.1kV |
|
Accuracy |
±2%of reading±0.2kV |
|
Voltage Ramp Rate |
0.5 /1.0 /2.0 / 3.0kV/s (selectable) |
|
Trip Time at Breakdown, ms |
≤1ms |
|
Test Repetitions |
1~6(selectable) |
|
Programmed test standard |
IEC60156/ASTM D877/ASTM D1816 |
|
Result Storage Capacity |
30 groups |
|
Oil Cup Capacity |
200ml standard; 300ml and 500 ml option |
|
Electrode Gap |
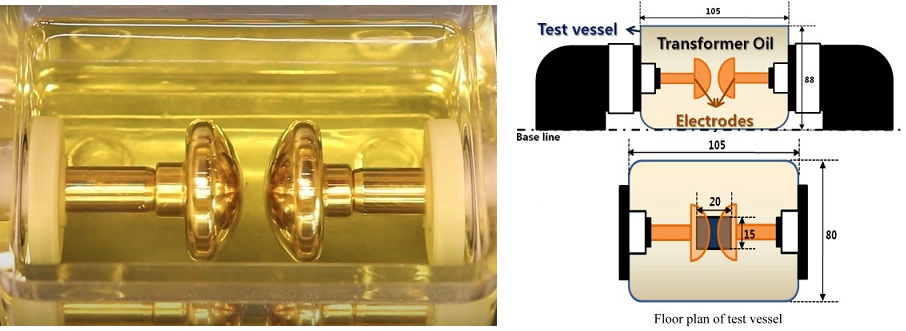
2.5 mm (Electrode gap is adjustable) |
|
Operation Temperature |
0~40℃ |
|
Relative Humidity |
≤ 80%RH, no condensation |
|
Power supply |
AC220V±10%, 50Hz±1% |
|
Dimensions / Weight |
Length 409 mm Width 393 mm Height 388 mm / 29kgs |
1. Clean and dry the oil test cup, standard gauge, glass rod for stirring and glass plate for covering the oil cup.

3. Rinse the oil cup three times with the sample oil. Use a gauge to adjust the distance between the electrodes of the oil cup (2.5 mm), then slowly inject the test oil into the oil cup along the stirring glass rod until it is ≥10 mm above the electrode, then cover the glass cover and let it stand still for 15 minutes to make the air bubbles in the oil overflow.

4. Then turn on the power supply, and increase the voltage evenly at a speed of 3~5kV/s until the oil cup electrode breaks down, and (KOF overcurrent trip) disconnect the power supply.

5. Use a stirring glass rod (about 2 mm in diameter) to gently move between the electrodes to remove carbon particles on the surface of the electrodes due to breakdown.
6. After stirring, stand still for 5 minutes and pressurize again.7. The breakdown should be repeated six times in total, the first time is not calculated, and the average value of the five breakdowns is taken as the final oil pressure resistance value.
8. If insulating oil BDV value is above 30 KV, transformer oil is good.

Kingrun Transformer Instrument Co.,Ltd.




More Transformer Testers from Kingrun
