⚡ Current Transformer (CT) Facts
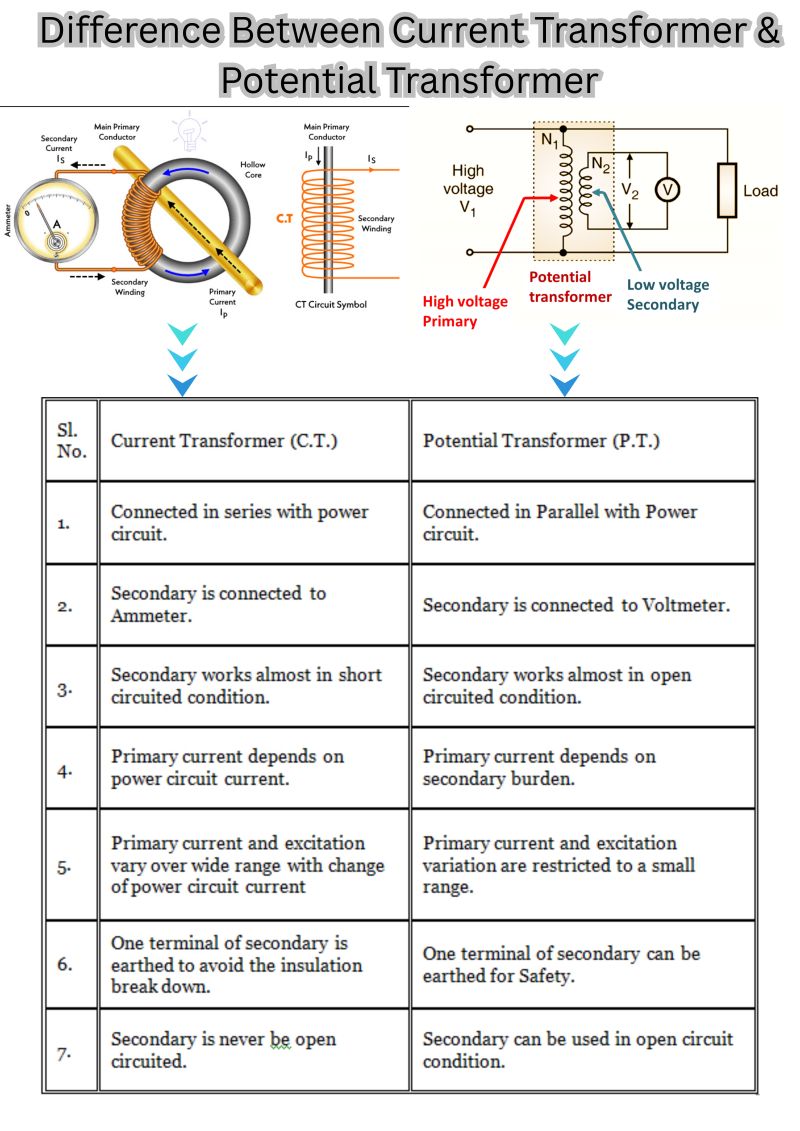
CT (Current Transformer)is used to measure high current by producing a proportionally smaller current.
It is connected in series with the load.
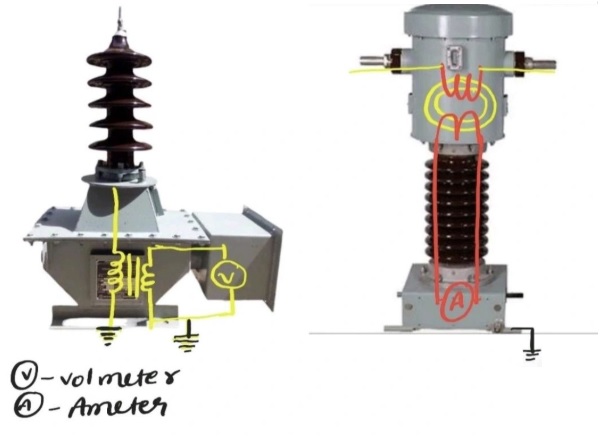
⚡ Potential Transformer (PT) Facts
PT (also called VT – Voltage Transformer) is used to measure high voltage.
It is connected in parallel to the circuit.
PT steps down high voltage to a standard value like 110V or 63.5V.
Provides voltage inputs to meters, relays, and control devices.
Accuracy class is defined (e.g., 0.1, 0.2, 0.5) for precision measurement.
Secondary should never be short-circuited.
Uses high dielectric insulation due to high voltage exposure.
Core is designed to work under low magnetic flux to avoid saturation.
Used in voltage protection, synchronizing, and metering applications.
Kingrun Transformer Instrument Co.,Ltd.



More Transformer Testers from Kingrun
