This parameter directly indicates the accuracy of the winding turns and the integrity of the magnetic coupling structure. Any deviation from the design ratio may imply shorted turns, open circuits, incorrect connections, or winding displacement. Therefore, the turn ratio test is essential for ensuring reliable transformer performance and detecting potential winding faults.
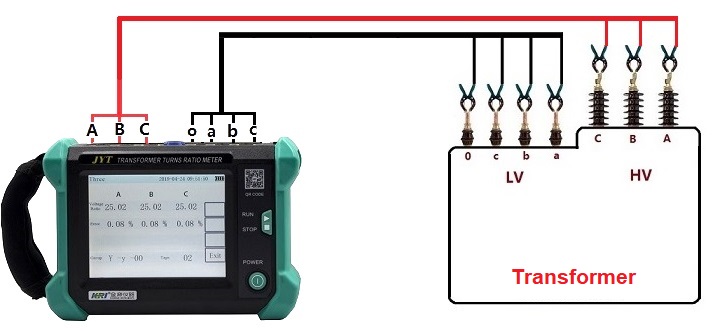
Magnetic coupling – The precision of the voltage ratio measurement depends on maintaining clean and symmetrical connections; uneven or twisted long leads may cause phase shift errors.

3. Recommended Lead Lengths:
|
Transformer Type |
Recommended Lead Length (per side) |
Notes |
|
Small distribution transformers (≤ 630 kVA) |
≤ 3–5 m |
Keep the tester close to the transformer to minimize lead resistance. |
|
Medium transformers (800–3150 kVA) |
≤ 8–10 m |
Use leads with a cross-section of ≥ 4 mm². |
|
Large power transformers (≥ 4000 kVA) |
≤ 10–15 m |
Use 6~10 mm² thick copper leads; if necessary, extend current leads but keep potential leads short. |
Environmental considerations: Avoid strong electromagnetic fields and vibration sources near the test area.
The 5 Most Popular transformer turn ratio testers in the World
What is the Difference between "Ratio" and "Turn Ratio" in a Transformer Testing?
How to Choose the Right Turns Ratio of CT/PT?
Why is it so Important to Test Transformer Turn Ratio?
What are the Reasons for Abnormal Voltage Output of Power Transformers?
More Transformer Testers from Kingrun

Kingrun Transformer Instrument Co.,Ltd.


