When actually measuring the contact resistance of the contacts of the electrical connector, it is all carried out at the lead-out end of the contact, so the actual measured contact resistance also includes the conductor resistance of the contacts outside the contact surface and the lead wire itself. The conductor resistance mainly depends on the electrical conductivity of the metal material itself, and its relationship with the ambient temperature can be characterized by a temperature coefficient.
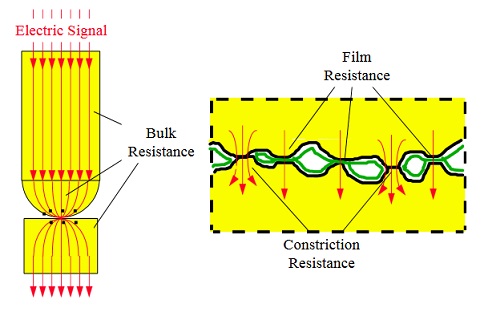

As one of the most important characteristic indicators in the electrical parameters of switchgear, contact resistance is the key information for early warning of abnormal power supply and the most reliable indicator of power system performance and decay. In assessing reliability and predicting failure of most types of power connections, including circuit breakers, disconnectors, load switches, etc., the stability test of contact resistance is the most effective. The magnitude of the contact resistance directly affects the through-load rating of the circuit breaker. Temperature rise at operating current and dynamic and thermal stability under short-circuit conditions. The change of the contact resistance value will also directly affect the reliability of the circuit breaker and the safety of the circuit breaker operation. Specifically, if the circuit resistance of the circuit breaker increases for some reason, it will break the original thermal balance and increase the temperature rise of the contact part, thereby increasing the resistivity of the conductor and further increasing the heat generation. The operation of the circuit breaker under the condition of high current will cause oxidation of the contact surface, softening or aging of the supporting insulator, resulting in the failure of the circuit breaker, making it unable to work normally in the short-circuit state.
Other Related Articles:
Why Does the Contact Resistance Testing Need 100A or Higher?
Hazards and Treatment of Excessive Contact Resistance of Circuit Breakers or HV Switches
How to measure the contact resistance without changing the circuit?
How to Correctly Test the Contact Resistance of HV Switchgear or Circuit Breaker?
Why Does Excessive Contact Resistance Occur In Electrical Secondary Circuits?
What is the Testing Checklist for 110kV/220kV Substation Acceptance and Maintenance Testing?
Kingrun Transformer Instrument Co.,Ltd.



More Transformer Testers from Kingrun
