What Is the Temperature Rise (Heat-run) Test of a Transformer?
Transformer temperature rise testing is a procedure to evaluate the temperature increase of a transformer during operation. This testing determines the temperature rise of the transformer under different load conditions, ensuring it operates within a safe range to prevent failures or damage due to overheating. The temperature rise test typically involves the following steps:
Preparation: Connect the transformer to the testing equipment, ensuring all instruments are functioning properly.
Applying Load: Operate the transformer under various load levels and record the running time.
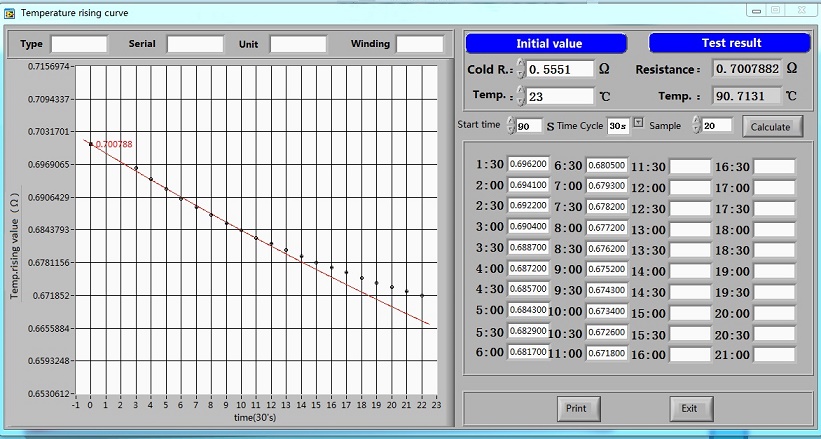
Measuring Temperature: Use temperature sensors to measure the temperature in the transformer windings and oil (if it's an oil-immersed transformer).
Data Analysis: Analyze the test data to calculate the temperature rise and compare it with standard values to assess the transformer's performance.
Do All Transformers Need Temperature Rise Testing?
Not all transformers require temperature rise testing. Generally, temperature rise testing is primarily for the following types of transformers:
Large or High-Power Transformers: These transformers generate significant heat under load and must monitor their temperature rise to ensure safety.
Oil-Immersed Transformers: Due to the characteristics of the oil cooling system, regular temperature rise testing is necessary.
Dry-Type Transformers: Temperature rise must be monitored, especially under high load conditions.
Newly Installed or Significantly Maintained Transformers: Testing is needed to confirm performance under actual operating conditions.
For small, low-power, or non-critical application transformers, temperature rise testing is often unnecessary. However, in specific cases, such as prolonged high loads or harsh environmental conditions, temperature monitoring may be considered.
Related Articles:
The Most Complete Transformer Vector Group Collection with Winding Connection Diagrams
How Important is Transformer DC Winding Resistance?
Top 6 transformer winding resistance testers Worldwide (Including Prices)
How should Winding Resistance be Tested Differently on CT and PT?
What is the Difference between DC Resistance and Insulation Resistance and How to Test Them?
8 Tips to Improve the Accuracy of DC Resistance Measurement
Why is the Tested Winding Resistance Always Inaccurate? You May Have Overlooked These 6 Key Points
Kingrun Series DC winding resistance testers

Kingrun Transformer Instrument Co.,Ltd.



More Transformer Testers from Kingrun
