In the operation and maintenance of electrical equipment, contact resistance and winding resistance are two key parameters, often confused because they are both related to "resistance." The former concerns connection reliability, while the latter affects the core performance of the equipment; their nature and characteristics differ significantly.
Contact resistance refers to the resistance generated at the electrical connection point formed by two conductors through mechanical contact; it is essentially interface resistance. It is not an inherent property of the conductor itself, but is determined by the physical state of the contact interface (such as pressure, flatness, oxide layer), and is commonly found in detachable or movable electrical connections such as connectors, switches, relay contacts, and terminals. For example, the resistance between the contact points of a plug and socket, and between the moving and stationary contacts of a circuit breaker, are contact resistance.
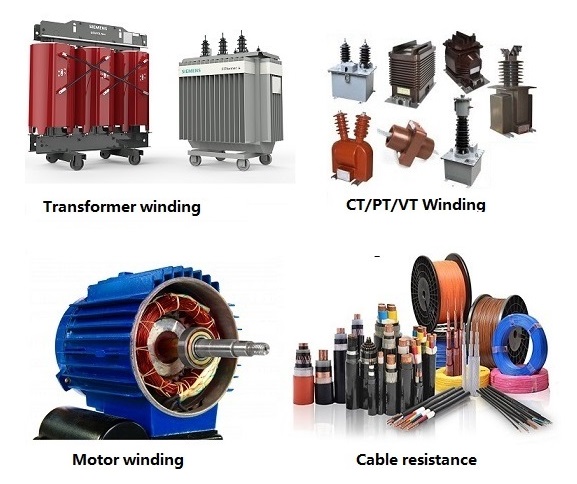
Winding resistance refers to the DC resistance inherent in the windings formed by the conductors in electrical equipment such as motors, transformers, and inductors; it is essentially the inherent resistance of the conductor. It is determined by the material (such as copper or aluminum), cross-sectional area, length and operating temperature of the winding conductor. It is an inherent parameter in the equipment design and reflects the conductivity of the winding conductor. For example, the resistance of the stator winding of a motor and the primary and secondary windings of a transformer are both winding resistances.

Related Artical: Contact Resistance VS Loop Resistance
Application Scenarios and Practical Significance
1.Key Applications of Contact Resistance:
Primarily used to assess the reliability of electrical connections. For example:
* The contact resistance of high-voltage circuit breakers in power systems needs to be regularly checked to ensure normal opening and closing;
* Excessive contact resistance in automotive wiring harness connectors can lead to dimming lights and starting failures;
* The contact resistance of connectors in electronic devices (such as USB interfaces and board-to-board connectors) affects signal transmission stability.
2.Key Applications of Winding Resistance:
Primarily used in equipment design, performance evaluation, and fault diagnosis. For example:
* Transformers require measurement of the primary and secondary winding resistances at the factory to verify whether the conductor specifications and winding process meet the design requirements;
* During motor maintenance, comparing winding resistance values helps determine if there are inter-turn short circuits, winding imbalances, or other problems;
* The winding resistance of inductors affects their Q value (quality factor), which in turn affects the performance of filtering and resonant circuits.
What are the differences between a Contact Resistance Tester and a winding resistance tester?
The function of DC winding resistance tester is to detect the winding resistance of transformers, motors and other windings, this instrument circuit will exist inductive reactance or capacitive reactance, so it is impossible to enter the high-current test, unless the instrument has a large capacity of the test device, otherwise it is difficult to use.
The general resistance value of the contact resistance tester is very small, which is microohm level, which refers to the on-contact resistance of the disconnector and circuit breaker. However, the contacts of these devices are prone to oxidation. Therefore, the oxide film must be destroyed after the large current is passed during the detection, so that the true DC resistance value of the circuit can be tested. There is no impedance in this curcuit, so the resistance can be quickly measured once the current is applied.
These two testers are used to test resistance, in the method are the use of DC voltage drop method, there are many people who do not understand this will think that it is the same, can be used interchangeably, but in essence there is still a difference between the two, from the test product, loop resistance tester test is mainly resistive load, and are microresistance test, DC resistance tester test is mainly inductive load, resistive range is relatively large, the two can not be used interchangeably, for example, If a loop resistance tester is used to measure the inductive load, it will damage the equipment. At present, there are still no two instruments on the market of synthetic type, if you want to combine two devices into one device, then you have to meet the high current, but also to meet the test resistance relatively large inductive load, so that it is more troublesome, and the cost is also very high, the equipment volume is also very large.
Why Does the Contact Resistance Testing Need 100A or Higher?
Kingrun Transformer Instrument Co.,Ltd.



More Transformer Testers from Kingrun
